
Exploring the realm of Universal Healthcare Access, this introduction sets the stage for a deep dive into the importance of providing healthcare to everyone, highlighting key aspects and challenges with a captivating narrative.
As we delve further into the intricacies of healthcare systems worldwide, the complexities and benefits of universal healthcare access become clearer, shaping our understanding of its significance in today’s society.
Healthcare Access
Universal healthcare access refers to a system where all individuals in a society have access to essential healthcare services without facing financial hardship. This ensures that everyone, regardless of their income level or social status, can receive necessary medical care when needed.
Countries with Successful Universal Healthcare Systems
- Canada: Known for its publicly funded healthcare system, providing coverage for medically necessary services to all citizens.
- United Kingdom: The National Health Service (NHS) offers comprehensive healthcare services to residents, funded through taxation.
- Australia: Operates a universal healthcare system called Medicare, which covers a wide range of medical services for its citizens.
Benefits of Ensuring Healthcare Access for All Individuals
- Improved Health Outcomes: Access to healthcare services helps prevent and manage diseases, leading to better overall health in the population.
- Economic Stability: By ensuring healthcare access, individuals are more likely to stay healthy and productive, contributing to a stable economy.
- Reduced Health Disparities: Universal healthcare can help address inequalities in healthcare access based on income or social factors.
Impact of Universal Healthcare Access on Public Health Outcomes
- Lower Mortality Rates: Countries with universal healthcare systems tend to have lower mortality rates due to better access to preventive care and treatments.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By providing access to healthcare early on, overall healthcare costs can be reduced as individuals are less likely to require expensive treatments for advanced illnesses.
- Healthier Population: Universal healthcare access leads to a healthier population overall, with individuals being able to address health concerns promptly and effectively.
Healthcare Costs
The rising costs of healthcare are influenced by various factors, including advances in medical technology, administrative expenses, pharmaceutical costs, an aging population, and an increase in chronic diseases. These factors contribute to the overall increase in healthcare spending, making it a significant challenge for individuals and governments alike.
Strategies to Reduce Healthcare Costs
- Implementing preventive care measures to reduce the incidence of costly diseases.
- Encouraging the use of generic medications to lower pharmaceutical costs.
- Implementing cost-effective treatment protocols and guidelines.
- Investing in healthcare infrastructure to improve efficiency and reduce overhead costs.
Economic Implications of Universal Healthcare Access
Universal healthcare access can have both positive and negative economic implications. On one hand, providing healthcare to all citizens can lead to a healthier and more productive workforce, reducing absenteeism and increasing economic output. On the other hand, the costs of implementing and maintaining a universal healthcare system can be substantial and may require increased taxation or reallocation of funds from other government programs.
Relationship Between Healthcare Costs and Quality of Care
The relationship between healthcare costs and the quality of care is complex and varies across different healthcare systems. While higher healthcare costs may sometimes be associated with better quality of care, this is not always the case. In some instances, high costs may be driven by inefficiencies or unnecessary procedures, leading to lower value for patients. It is essential for healthcare systems to strike a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in ensuring universal healthcare access by delivering essential medical services to individuals regardless of their background, income, or location.
Challenges Faced by Healthcare Providers
- Unequal distribution of healthcare professionals in rural and urban areas, leading to limited access to care for some populations.
- Financial constraints impacting the ability of healthcare providers to offer quality services to all patients.
- Inadequate training and resources for healthcare professionals to address the diverse needs of patients.
Initiatives Addressing Disparities in Healthcare Provider Distribution
- Telemedicine programs that connect patients in underserved areas with healthcare providers remotely.
- Scholarship and loan forgiveness programs to incentivize healthcare professionals to work in underserved communities.
- Government-funded initiatives to build more healthcare facilities in areas with limited access to medical services.
Importance of Training and Retaining Healthcare Professionals
- Continuous training ensures that healthcare providers stay updated with the latest medical practices and technologies.
- Retaining experienced healthcare professionals in the system helps maintain consistency and quality of care for patients.
- Investing in the well-being and professional development of healthcare professionals leads to higher job satisfaction and better patient outcomes.
Health Insurance
Health insurance plays a crucial role in achieving universal healthcare access by providing individuals with financial protection against high healthcare costs. It helps individuals afford necessary medical services, medications, and treatments without facing significant financial burden or barriers to access.
Comparison of Health Insurance Models
Different models of health insurance exist within universal healthcare systems, including single-payer systems, multi-payer systems, and social health insurance. Single-payer systems, like in Canada, involve a single government-run insurance program that covers all residents. Multi-payer systems, like in Germany, have multiple insurance funds that compete to provide coverage. Social health insurance, like in France, involves mandatory contributions from both employers and employees to finance healthcare.
Impact of Insurance Coverage on Healthcare Utilization and Health Outcomes
Insurance coverage has been shown to increase healthcare utilization by allowing individuals to seek necessary medical care without worrying about costs. This, in turn, can lead to better health outcomes as individuals are more likely to receive preventive care, early interventions, and ongoing treatments for chronic conditions.
Challenges of Ensuring Comprehensive Health Insurance Coverage
Ensuring comprehensive health insurance coverage for all individuals poses several challenges, including affordability, accessibility, and equity. Some individuals may still face barriers to obtaining coverage due to costs, eligibility criteria, or lack of awareness about available options. Additionally, disparities in coverage can exist based on income, employment status, or geographic location, highlighting the need for policies that address these inequities.
Health Policies
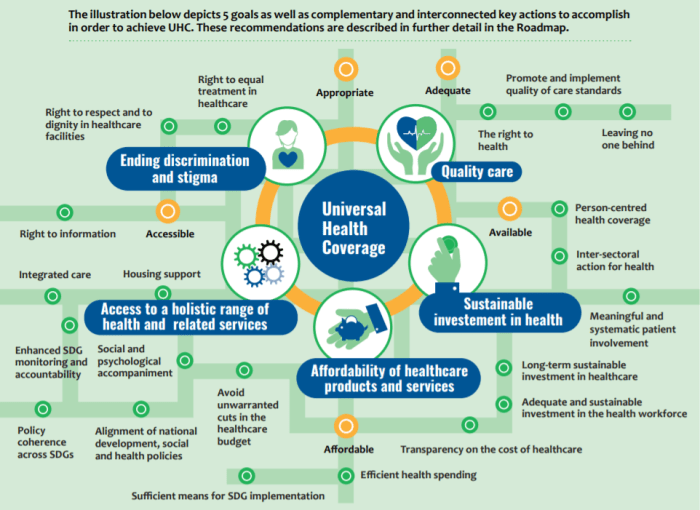
Health policies play a crucial role in supporting universal healthcare access by outlining guidelines and regulations to ensure equitable and affordable healthcare for all individuals.
Key Health Policies for Universal Healthcare Access
- Implementation of mandatory health insurance coverage to reduce financial barriers to healthcare services.
- Expansion of Medicaid and Medicare programs to provide coverage for low-income individuals and seniors.
- Regulation of healthcare costs to prevent price gouging and ensure affordability for all patients.
Government’s Role in Healthcare Policy
- The government plays a pivotal role in developing and implementing healthcare policies to safeguard the well-being of its citizens.
- Government interventions through legislation and regulatory frameworks help in structuring healthcare systems to prioritize accessibility and quality of care.
Successful Policy Interventions for Improved Healthcare Access
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States significantly increased the number of insured individuals and improved healthcare access for millions.
- The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom provides universal healthcare coverage, ensuring access to essential services for all residents.
Effectiveness of Policy Incentives in Promoting Universal Healthcare Coverage
- Policy incentives such as tax credits for health insurance premiums can encourage individuals to enroll in coverage, expanding the insured population.
- Incentivizing healthcare providers to offer services in underserved areas through subsidies or loan forgiveness programs can enhance access to care in remote regions.
Health Records
Electronic health records play a crucial role in universal healthcare systems by providing a centralized digital platform for storing and managing patient information. This allows healthcare providers to access a patient’s medical history, treatment plans, medications, and test results, leading to more efficient and coordinated care.
Benefits of Integrated Health Records
Integrated health records streamline communication between different healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of a patient’s care team have access to the same information. This leads to better care coordination, reduced medical errors, and improved patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Patient Care: Integrated health records enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions quickly, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans.
- Efficient Workflow: By having access to a patient’s complete medical history, providers can avoid redundant tests and procedures, saving time and resources.
- Improved Patient Safety: Integrated health records help reduce errors in medication administration and treatment, enhancing patient safety and quality of care.
Privacy and Security Concerns
While the benefits of electronic health records are significant, there are concerns regarding the privacy and security of patient information. Safeguards must be in place to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches, ensuring patient confidentiality and trust in the healthcare system.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to health records can result in identity theft, fraud, and other malicious activities, compromising patient privacy.
- Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare providers must adhere to strict data protection regulations to safeguard patient information and maintain trust in the healthcare system.
- Secure Technology: Implementing secure encryption methods and access controls is essential to prevent data breaches and ensure the confidentiality of health records.
Efficient Health Record Systems in Countries
Countries like Estonia, Singapore, and Australia have efficient health record systems that support universal healthcare access by providing a centralized platform for storing and sharing patient information securely. These systems enhance care coordination, reduce medical errors, and improve overall healthcare outcomes for their populations.
Health Screening

Health screening programs play a crucial role in universal healthcare systems by focusing on early detection and prevention of diseases.
Common Health Screening Initiatives
- Regular blood pressure checks
- Cholesterol level screenings
- Mammograms for breast cancer detection
- Colonoscopies for colon cancer screening
Impact of Preventive Screenings
Preventive screenings not only help in detecting diseases in their early stages but also contribute to reducing healthcare costs in the long run. By addressing health issues proactively, individuals can avoid more expensive treatments that may be required for advanced stages of diseases.
Successful Health Screening Campaigns
- The “Know Your Numbers” campaign promoting regular blood pressure and cholesterol screenings.
- The “Pink October” initiative raising awareness about breast cancer screenings and mammograms.
- The “Fit to Test” program encouraging individuals to undergo regular HIV screenings for early detection.
In conclusion, the discussion on Universal Healthcare Access underscores the vital need for equitable healthcare for all individuals, emphasizing the transformative impact it can have on public health outcomes and societal well-being.
Essential FAQs
What are some challenges in implementing universal healthcare access?
One major challenge is funding the system adequately to ensure quality care for all individuals.
How does universal healthcare access impact public health outcomes?
Universal healthcare access can lead to improved health outcomes by providing timely and comprehensive care to all, thus reducing overall disease burden.
What role do health policies play in ensuring universal healthcare access?
Health policies are essential in creating a framework that supports and enables universal healthcare access by outlining regulations and guidelines for healthcare delivery.
Why is training and retaining healthcare professionals crucial in a universal healthcare system?
Ensuring a skilled and stable workforce of healthcare providers is vital to meet the healthcare needs of a growing population and maintain quality care standards.
How do health records contribute to improving care coordination in universal healthcare systems?
Integrated health records facilitate seamless sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, leading to better coordination of care and treatment outcomes.





